Container Homes: A Modern Living Option Worth Exploring
Shipping container homes provide a practical and innovative option for modern living. This article outlines how these homes are constructed, what to consider before choosing this style of housing, and key factors like design, permits, and potential cost benefits. It’s a helpful overview for anyone exploring alternative housing options.

What Exactly Are Shipping Container Homes?
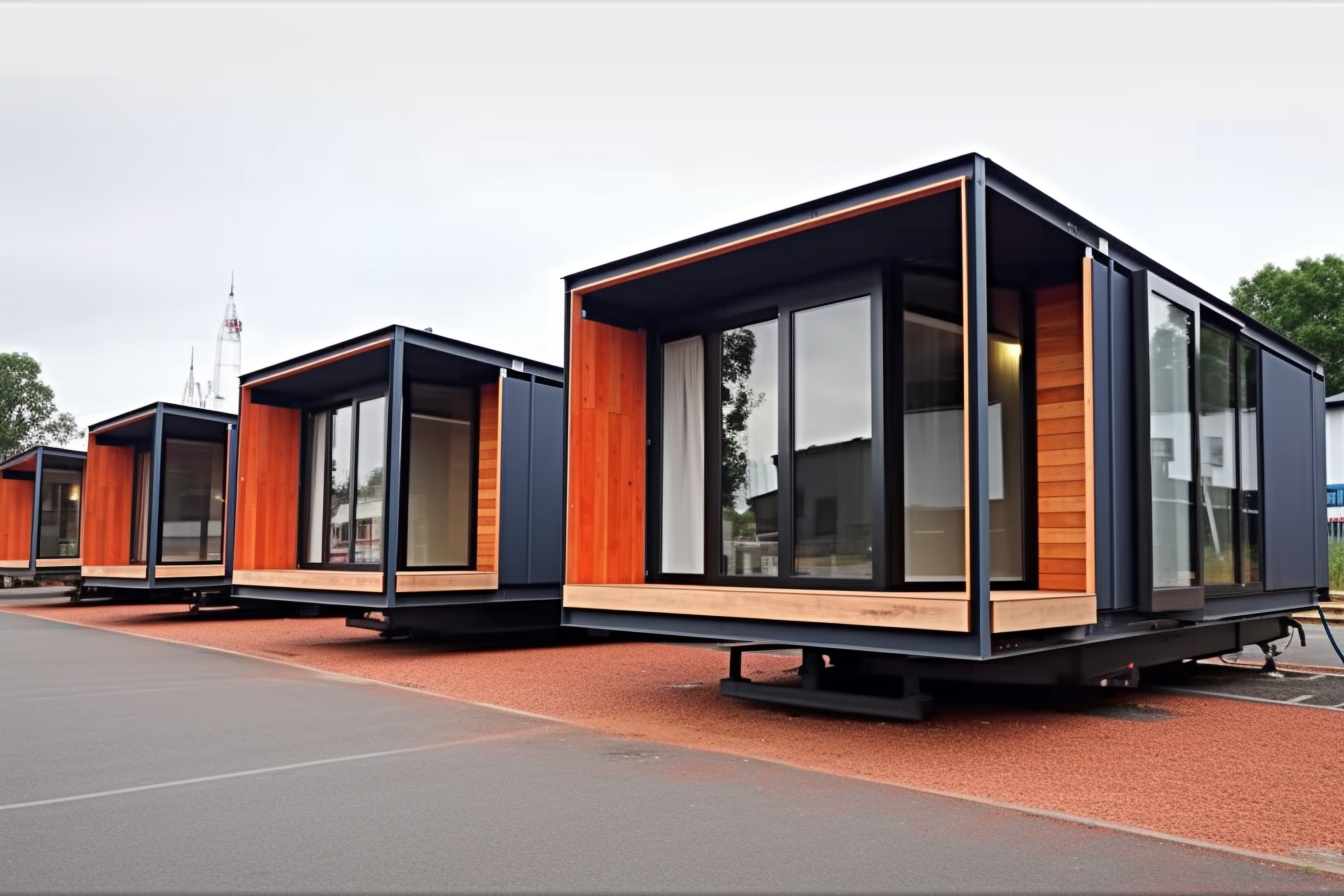
Shipping container homes are residential structures built partially or entirely from decommissioned shipping containers—the same steel boxes used to transport goods across oceans. These standardized containers typically come in 20-foot and 40-foot lengths, with standard heights of 8’6” (standard) or 9’6” (high cube). The inherent strength of these containers—designed to withstand harsh ocean conditions and heavy stacking—provides a robust structural foundation for housing. The concept gained traction in the early 2000s as part of the broader architectural movement toward adaptive reuse and sustainable building practices. Today, container homes range from simple, single-container tiny homes to elaborate multi-container mansions featuring all the amenities of traditional housing.
How Are Container Homes Constructed?
The construction process for container homes begins with selecting appropriate containers—ideally those in good condition with minimal rust or structural damage. The basic construction process typically follows these steps:
-
Container preparation: Removing any harmful chemicals, sandblasting, and treating the steel to prevent corrosion
-
Structural modifications: Cutting openings for doors, windows, and connections between multiple containers
-
Reinforcement: Adding support where necessary, especially around large openings
-
Insulation: Installing appropriate insulation to manage temperature extremes
-
Interior finishing: Adding interior walls, flooring, plumbing, electrical systems, and other home essentials
Construction methods vary based on climate, local building codes, and design preferences. Some builders preserve the industrial aesthetic of the containers, while others completely transform their appearance. Professional container home builders typically use specialized tools for cutting and welding the corrugated steel walls. The modular nature of containers allows for both on-site and off-site construction, with some companies prefabricating container homes in factories before delivery to the building site.
What Are The Benefits Of Living In A Container Home?
Container homes offer several compelling advantages that have contributed to their growing popularity:
Sustainability: Repurposing shipping containers reduces waste and extends the lifecycle of these industrial products. Each reused container prevents approximately 7,700 pounds of steel from entering the waste stream. Additionally, the smaller footprint of many container homes often results in reduced energy consumption.
Durability: Built to withstand ocean transport, extreme weather, and stacking loads, shipping containers provide exceptional structural integrity. Their weatherproof steel construction offers natural resistance to fire, mold, and pests when properly maintained.
Speed of construction: Container homes typically require significantly less construction time than traditional homes. With much of the structural work already complete, build times can be reduced by 30-50% compared to conventional construction.
Flexibility and modularity: The standardized dimensions of shipping containers create nearly endless possibilities for expansion and reconfiguration. Homeowners can start small and add additional containers as needs change or budgets allow.
Potential cost savings: Depending on design complexity and location, container homes can be more affordable than traditional construction, particularly for those willing to incorporate DIY elements or opt for simpler designs.
What Challenges Might Container Home Owners Face?
Despite their advantages, container homes present several challenges that prospective owners should carefully consider:
Insulation and temperature regulation: Steel conducts heat and cold efficiently, making proper insulation crucial but challenging. Without adequate thermal management, container homes can become uncomfortably hot or cold. Insulation also reduces interior space, a significant consideration in already compact containers.
Building code compliance: Many municipalities lack specific codes for container homes, creating potential regulatory hurdles. Some areas require extensive engineering documentation or special permits, increasing both costs and timeline.
Potential for toxic materials: Shipping containers may contain harmful chemicals from manufacturing or transport use. Flooring may be treated with pesticides, while paints may contain heavy metals. Professional testing and remediation are often necessary safety precautions.
Limited interior space: Standard shipping containers offer relatively narrow interior dimensions (7’8” wide for standard containers), creating design constraints. Structural modifications to create more open spaces often require additional reinforcement and engineering expertise.
Humidity and condensation: The temperature difference between the steel exterior and interior can create condensation problems within walls, potentially leading to mold and corrosion if not properly addressed through ventilation and moisture barriers.
What Are Some Popular Design Ideas For Container Homes?
Creative architects and homeowners have developed numerous innovative approaches to container home design:
Stacked configurations: Placing containers in various arrangements creates multi-level homes with interesting visual elements. Offsetting upper containers creates natural overhangs and outdoor spaces, while strategic stacking can maximize views and create architectural interest.
Mixed materials: Combining container elements with traditional construction materials softens the industrial aesthetic. Wood cladding, large windows, and conventional roofing can transform the appearance while maintaining structural benefits.
Courtyard designs: Arranging containers in U or L shapes creates protected outdoor living spaces. This approach is particularly effective in temperate climates where indoor-outdoor living is desirable.
Roof gardens and green roofs: The flat roofs of containers provide excellent opportunities for rooftop gardens or green roof systems, improving insulation while creating usable outdoor space.
Cantilever designs: Extending portions of containers beyond their support points creates dramatic overhangs and architectural interest. When properly engineered, these designs can provide shade, visual appeal, and expanded interior space.
Container Home Cost Considerations
The cost of container homes varies significantly based on design complexity, location, and whether professional builders or DIY methods are employed. Basic container home projects typically range from $10,000 to $35,000 per container for minimal conversions. Mid-range projects incorporating better finishes and more extensive modifications generally cost between $50,000 and $125,000, while luxury container homes with high-end materials can exceed $200,000.
| Type of Container Home | Approximate Cost Range | Key Cost Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Single Container | $10,000 - $35,000 | DIY labor, minimal insulation, simple utilities |
| Mid-Range Multi-Container | $50,000 - $125,000 | Professional construction, standard finishes, moderate modifications |
| Luxury Container Home | $150,000 - $300,000+ | Extensive structural modifications, high-end materials, complex systems |
| Container Home Kit | $15,000 - $60,000 | Pre-cut openings, basic plans, some materials included |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Shipping container homes represent a unique intersection of industrial heritage and residential innovation. While they offer numerous benefits in sustainability, durability, and design flexibility, they also present distinct challenges that require careful planning and sometimes specialized expertise. As building techniques evolve and more municipalities develop specific codes for these structures, container homes will likely continue to expand beyond their current niche, offering an intriguing alternative in the housing landscape.