Scalp Psoriasis Explained: What Causes It and How to Treat It
Dealing with constant itching, flaking, or thick patches on your scalp? It could be more than dandruff—it might be scalp psoriasis. This common autoimmune condition can lead to irritation, embarrassment, and even hair thinning if ignored. In this guide, you'll discover what causes it, how to spot early symptoms, and which soothing treatments actually work. Whether you're newly diagnosed or tired of recurring flare-ups, here’s your path to a calmer, healthier scalp.
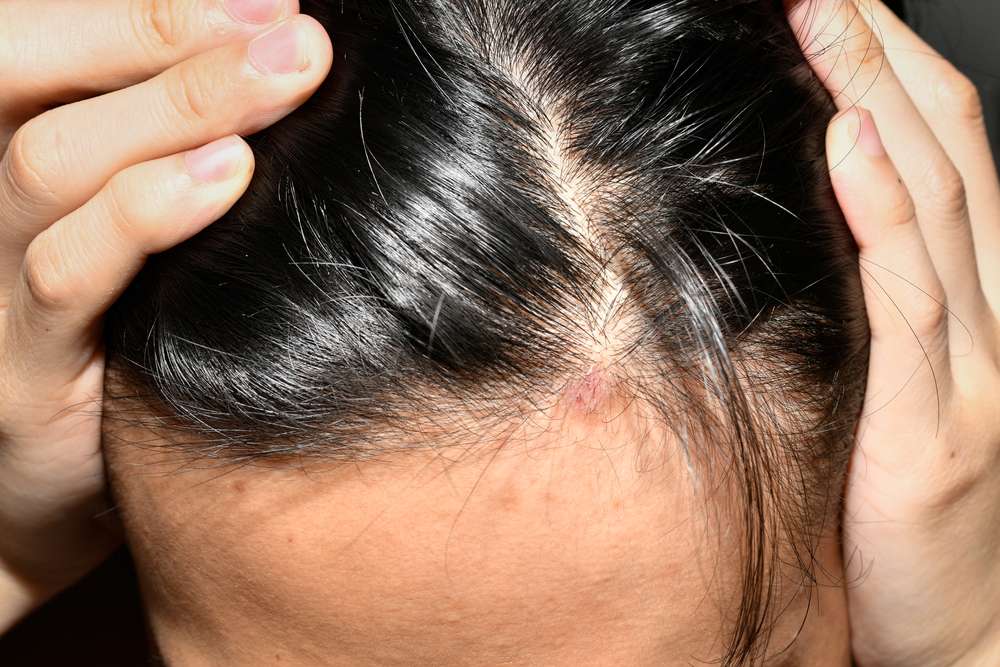
Root Causes and Triggers of Scalp Psoriasis
Scalp psoriasis, like other forms of psoriasis, is fundamentally an autoimmune condition where the immune system accelerates skin cell growth. Normal skin cells typically grow and shed over a month, but in psoriasis, this process happens in just days, causing cells to build up and form scaly patches. Several factors contribute to the development and flare-ups of scalp psoriasis:
Genetic predisposition plays a significant role, with approximately 40% of patients having a family history of the condition. Environmental triggers often exacerbate symptoms, including stress, cold weather, certain medications (like beta-blockers and lithium), and skin injuries. Hormonal changes can also influence the condition, which explains why many patients experience their first symptoms during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause. Additionally, certain lifestyle factors such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and obesity can increase the severity and frequency of flare-ups.
What Are the Visual Signs Found in Psoriasis Pictures
Identifying scalp psoriasis begins with recognizing its distinctive visual characteristics. The condition typically presents as red, inflamed patches covered with silvery-white scales. These patches can appear anywhere on the scalp, from small, isolated spots to widespread areas that extend beyond the hairline. In severe cases, temporary hair loss may occur due to aggressive scratching or harsh treatments.
Unlike common dandruff, which produces fine white flakes, scalp psoriasis flakes are thicker and more adherent to the scalp. The affected skin often appears raised and thickened, a condition known as plaque formation. Another visual indication is the “Auspitz sign”—when scales are removed, tiny blood droplets may appear on the surface. In more severe cases, cracks or fissures might develop in the skin, which can be painful and susceptible to infection. During flare-ups, increased redness, inflammation, and scaling are typically observed, making the condition more visually apparent.
Understanding Pictures of Plaque Psoriasis on the Scalp
Plaque psoriasis is the most common form affecting the scalp, characterized by clearly defined, raised red patches (plaques) covered with a buildup of dead skin cells appearing as silvery-white scales. These plaques can vary in size from small coin-sized lesions to large patches covering substantial areas of the scalp. The boundary between affected and unaffected skin is usually well-defined, creating a stark contrast visible in clinical images.
When examining pictures of scalp psoriasis, one might notice how the plaques can extend beyond the hairline, affecting the forehead, back of the neck, or behind the ears. This extension is a distinctive diagnostic feature. Medical photography also reveals how scalp psoriasis can appear differently depending on hair type and skin tone—in darker skin tones, plaques may appear purple or brownish rather than red, with scales that are more yellowed than white. Understanding these visual variations is crucial for proper diagnosis, as scalp psoriasis can sometimes be confused with seborrheic dermatitis or other scalp conditions.
Why Scalp Psoriasis Picking Worsens the Condition
The intense itching associated with scalp psoriasis often leads patients to scratch or pick at the scales, which creates a damaging cycle that exacerbates the condition. When a person picks at psoriasis plaques, they create micro-injuries to the skin, triggering what dermatologists call the “Koebner phenomenon”—where new psoriasis lesions develop at sites of trauma. This response is part of the body’s disordered immune reaction characteristic of psoriasis.
Additionally, picking removes the protective barrier of the skin, potentially introducing bacteria and causing secondary infections. The inflammation from these infections further triggers the immune response, leading to more psoriasis plaques. Research indicates that approximately 50% of people with psoriasis experience the Koebner phenomenon after skin trauma. Breaking the itch-scratch cycle is essential for management, often requiring both behavioral approaches and medical treatments to reduce inflammation and itching. Patients are advised to use gentle scalp massages instead of scratching and to keep fingernails short to minimize damage if scratching does occur.
Treatment Options and Management Strategies
Managing scalp psoriasis requires a multi-faceted approach tailored to the severity of the condition and individual response to treatments. The treatment pyramid typically begins with topical therapies, which are the first line of defense for mild to moderate cases:
Medicated shampoos containing active ingredients such as salicylic acid help remove scales, while coal tar reduces inflammation and slows skin cell growth. Topical corticosteroids are effective anti-inflammatory agents available in various strengths, from over-the-counter hydrocortisone to prescription-strength formulations. For moderate to severe cases, vitamin D analogs like calcipotriene help normalize skin cell production, often prescribed in combination with corticosteroids for enhanced efficacy.
When topical treatments prove insufficient, systemic medications may be necessary. These include oral retinoids, methotrexate, cyclosporine, and newer biologic drugs that target specific components of the immune system. Phototherapy, which involves exposing the skin to controlled amounts of ultraviolet light, can also be effective, particularly narrow-band UVB treatment.
Beyond medical treatments, lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing scalp psoriasis. Stress reduction techniques, maintaining a healthy weight, limiting alcohol consumption, and smoking cessation can all help reduce flare-up frequency and severity. Regular scalp care with gentle, fragrance-free products is also essential to prevent irritation.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.