Unraveling the Potential of Low Earth Orbit (LEO) Satellites in Telecommunications
Telecommunication has transformed dramatically since the days when Alexander Graham Bell first patented the telephone in 1876. Fast forward to the 21st century, and we find ourselves relying on an intricate network of cables, towers, and satellites for our daily communication needs. One development that is currently under the radar but has the potential to revolutionize the telecommunications industry is Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites.
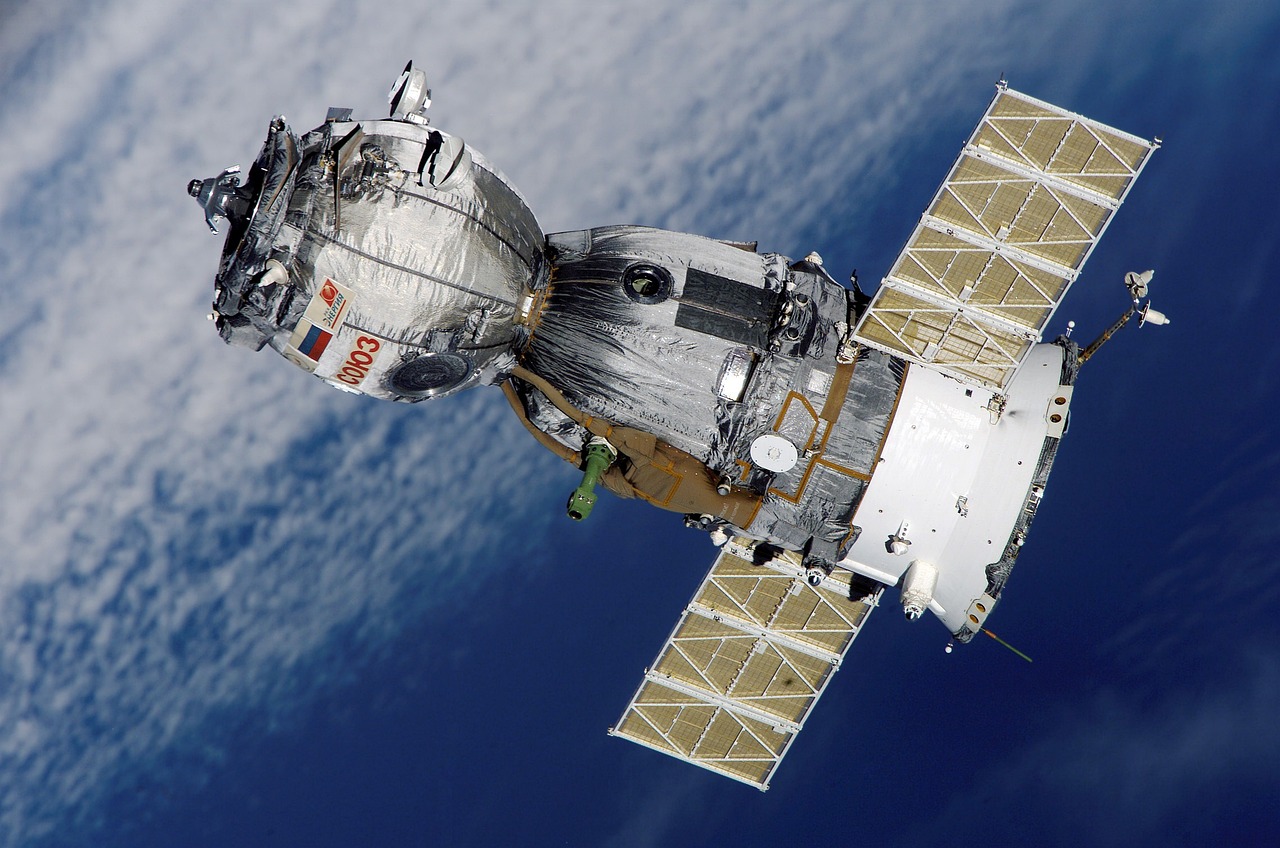

LEO satellites operate at an altitude of 2,000 kilometers or less above the earth’s surface, much closer than traditional geostationary satellites. This proximity brings about several advantages that can address some of the current challenges in the telecommunications industry. Let’s delve into the past, present, and future of LEO satellites.
Historical Context: The Birth of LEO Satellites
The concept of LEO satellites was first introduced in the 1980s, but it was not until the late 1990s that the first commercial LEO satellite, Iridium, was launched. Iridium’s initial goal was to provide phone services to remote areas without any terrestrial infrastructure. However, due to high operational costs and limited demand, the venture was not financially sustainable.
Despite this setback, the industry did not abandon the idea of using LEO satellites for telecommunication services. In the last decade, technological advancements have made it possible to manufacture and launch smaller, lighter, and cheaper satellites, reigniting interest in this domain.
Current Trends: The Resurgence of LEO Satellites
Today, several companies, including SpaceX, OneWeb, and Amazon, are planning to launch their own constellations of LEO satellites. These satellites aim to provide broadband internet service to all corners of the globe, even in rural and remote areas where terrestrial infrastructure is lacking.
Regulatory bodies are also adapting to these changes. The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the U.S., for instance, has approved several applications from companies seeking to launch LEO satellites.
Impact and Challenges: Weighing the Pros and Cons
The primary advantage of LEO satellites is their low latency. Since they are closer to the earth, data takes less time to travel, resulting in faster internet speeds. This is particularly beneficial for real-time applications like online gaming and video conferencing.
However, LEO satellites are not without their challenges. The sheer number of satellites needed to provide global coverage raises concerns about space debris and satellite collisions. There are also questions about the economic viability of such projects, given the high costs involved in launching and maintaining these satellites.
Practical Applications: Beyond Internet Services
While providing broadband internet services is the main goal of many LEO satellite operators, there are other potential uses as well. For instance, they can play a crucial role in disaster recovery by providing communication services when terrestrial infrastructure is damaged. They can also be used for earth observation, weather monitoring, and scientific research.
Conclusion
LEO satellites have the potential to reshape the telecommunications landscape by offering faster, more reliable internet services to all corners of the globe. However, this ambitious vision comes with significant challenges that need to be addressed. As we continue to push the boundaries of technology, it will be interesting to see how the story of LEO satellites unfolds.